This document lists the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 1.0 priority 1 and priority 2 checkpoints, and deliberately breaks the rules. The purpose of the document is to test whether commonly used accessibility validators successfully report all of the errors, and if not, how many they do successfully report. Some checkpoints are difficult to test, and validators may not attempt to test the content against the checkpoint. Others may be partially tested, such as ensuring that something is in place, with no regard to the relevance of what's in place.
There are 17 priority 1 checkpoints. There are no test cases for 6 of them.
Provide a text equivalent for every non-text element (e.g., via "
alt", "longdesc", or in element content). This includes: images, graphical representations of text (including symbols), image map regions, animations (e.g., animated GIFs), applets and programmatic objects, ascii art, frames, scripts, images used as list bullets, spacers, graphical buttons, sounds (played with or without user interaction), stand-alone audio files, audio tracks of video, and video.
This test is for the fairly common scenario where images are replaced, but the markup remains the same. The following image contains the text "Lemon", with a foreground colour very similar to the background colour. The alternative text provided is, "Apple".

Ensure that all information conveyed with color is also available without color, for example from context or markup
Items coloured red are incorrect.
Clearly identify changes in the natural language of a document's text and any text equivalents (e.g., captions).
I don't speak French, but I know that mon ami means my friend.
For data tables, identify row and column headers.
The following is a data table where the column headers have been marked up with th, but the row headers are marked up with td.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 |
| 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 |
| 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 28 | 32 | 36 | 40 |
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 |
| 6 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 42 | 48 | 54 | 60 |
| 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 49 | 56 | 63 | 70 |
| 8 | 16 | 24 | 32 | 40 | 48 | 56 | 64 | 72 | 80 |
| 9 | 18 | 27 | 36 | 45 | 54 | 63 | 72 | 81 | 90 |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
For data tables that have two or more logical levels of row or column headers, use markup to associate data cells and header cells.
The following table does not structure the headings correctly for the data.
| Gender | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | ||
| BBC | 8.2 | 9.1 | 17.3 |
| ITV | 16.3 | 2.2 | 18.5 |
Organize documents so they may be read without style sheets. For example, when an HTML document is rendered without associated style sheets, it must still be possible to read the document
The examples of relying on color alone should be picked up for this checkpoint. Another common example is to find background images with important information that is nowhere to be found in the content.
The interest rate is
Ensure that pages are usable when scripts, applets, or other programmatic objects are turned off or not supported. If this is not possible, provide equivalent information on an alternative accessible page.
Checkpoint 7.1 required authors to avoid content that flickers. As part of the tests, I've included a flashing image that can be stopped if scripting is available. If scripting isn't available, the animation cannot be turned off, with no alternative to stop the flashing image.
Until user agents allow users to control flickering, avoid causing the screen to flicker
Note: People with photosensitive epilepsy can have seizures triggered by flickering or flashing in the 4 to 59 flashes per second (Hertz) range with a peak sensitivity at 20 flashes per second as well as quick changes from dark to light (like strobe lights).
Obviously, I wouldn't want to cause anyone to have a seizure, so I've made the area of the image small, as the surface area needs to be large to cause photosensitive epilepsy. If you suffer, or suspect you suffer with photosensitive epilepsy, please don't go any further down this page without disabling images.
Are you sure you want to continue? If not, skip past the image to the test for clear language.
Last chance ...
Warning: Flashing image

Make programmatic elements such as scripts and applets directly accessible or compatible with assistive technologies [Priority 1 if functionality is important and not presented elsewhere, otherwise Priority 2.]
Unfortunately, whilst some assistive technologies have basic scripting support, most appear to have extremely poor support for changes to the DOM. The following paragraph has been inserted into the DOM with ECMAScript, with no alternative anywhere else on the page.
Update: Thank you to Jim Thatcher for pointing out that the script here is compatible with assistive technologies. When I have time, I'll replace this example for a scripting technique that isn't compatible with assistive technologies.
If, after best efforts, you cannot create an accessible page, provide a link to an alternative page that uses W3C technologies, is accessible, has equivalent information (or functionality), and is updated as often as the inaccessible (original) page.
This page does not adhere to WCAG 1.0, and no alternative has been provided.
Update: Thank you to Jim Thatcher for pointing out that the important part of this checkpoint is if you cannot create an accessible page, then provide a link to an alternative page. Jim is concerned that my interpretation is a common misinterpretation, but wrong, and he doesn't like to see the misinterpretation reinforced. I haven't interpreted the checkpoint the way Jim suggests, but as I agree with his point that this checkpoint is often misinterpreted, I've voiced his concerns so that I don't propagate the misinterpretation. I cannot make the page accessible for obvious reasons.
Use the clearest and simplest language appropriate for a site's content.
There was little evidence of myelencephala from this obnoxious quadragenarious with acute rhinotillexomania. Translation - an irritating 40 year old coward with a passion for picking their nose.
No test cases have been provided for the following priority 1 checkpoints:
[Back to Priority 1 Checkpoints | Back to the top of the page]
There are 29 priority 2 checkpoints. There are no test cases for 7 of them.
Ensure that foreground and background color combinations provide sufficient contrast when viewed by someone having color deficits or when viewed on a black and white screen. [Priority 2 for images, Priority 3 for text]
The following image has a background colour of #a70, with foreground text containing the phrase, "lemon", with a colour of #960.

The colour contrast analyser provides the following results for that colour combination:
The difference in brightness between the two colours is not sufficient. The threshold is 125, and the result of the foreground and background colours is 15.
The difference in colour between the two colours is not sufficient. The threshold is 500, and the result of the foreground and background colours is 34.
When an appropriate markup language exists, use markup rather than images to convey information
The following is the formula for calculating quadratic equations, which should be expressed in MathML.
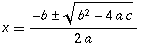
Create documents that validate to published formal grammars.
This document declares a DOCTYPE of HTML 4.01 Strict, which does not support the target attribute on links. The following link has a target attribute that has been added through DOM injection: Juicy Studio Home Page (opens in a new window).
Use style sheets to control layout and presentation.
This paragraph has an invalid align attribute with a value of right that has been added through DOM injection.
Use relative rather than absolute units in markup language attribute values and style sheet property values.
This text has a fixed font-size of 14pt.
Use header elements to convey document structure and use them according to specification.
h3Mark up lists and list items properly.
The following lists three guidelines recommended by the W3C's Web Accessibility Initiative, and is marked up incorrectly.
Mark up quotations. Do not use quotation markup for formatting effects such as indentation
The following text is not a quote.
This text isn't a quote. It's been marked up with
blockquotepurely to indent the text.
Do not use tables for layout unless the table makes sense when linearized. Otherwise, if the table does not make sense, provide an alternative equivalent (which may be a linearized version)
The following table is used for layout, does not make sense when linearised, and no alternative is provided.
This table is used purely for laying out the content. The table doesn't contain any structural markup such as caption, thead, tbody, tfoot, and th, but wouldn't make sense when the content is linearised, as one sentence would run in to the other.
|
Before deciding whether or not tables should make sense when linearised, it's worth reading the chapter on tables and frames from Joe Clark's book, Building Accessible Websites. |
If a table is used for layout, do not use any structural markup for the purpose of visual formatting.
The following table is used for layout, and uses structural markup.
| Structural Markup | Accessible Tables |
|---|---|
| End of table test | |
This table is used purely for laying out the content. The table contains structural markup such as caption, thead, tbody, tfoot, and th, and also uses the summary and scope attributes.
|
Before deciding whether or not tables should make sense when linearised, it's worth reading the chapter on tables and frames from Joe Clark's book, Building Accessible Websites. |
For scripts and applets, ensure that event handlers are input device-independent.
The link in the next paragraph has an event-handler for onclick inserted if scripting is supported and available. An equivalent event-handler has not been provided for onkeypress. Checkpoint 1.2 of the User Agent Accessibility Guidelines requires that event handlers are input device-independent (priority 2), so most modern user-agents will activate the event even though an explicit onkeypress event has not been provided.
Ensure that dynamic content is accessible or provide an alternative presentation or page.
The following dynamic content is not accessible, and there is no alternative for the content.
Until user agents allow users to control blinking, avoid causing content to blink (i.e., change presentation at a regular rate, such as turning on and off).
The test for dynamic content causes a blink effect by changing the presentation at a regular rate.
Until user agents allow users to freeze moving content, avoid movement in pages.
This content moves if scripting is available.
For scripts, specify logical event handlers rather than device-dependent event handlers.
This test is covered by the test for device-dependent event handlers, where the device-dependent event onclick has been specified.
Until user agents allow users to turn off spawned windows, do not cause pop-ups or other windows to appear and do not change the current window without informing the user.
The following link has an invalid target attribute that has been added through DOM injection, with no warning that it will open in a new window (discarding this preamble): Juicy Studio Home Page.
Until user agents support explicit associations between labels and form controls, for all form controls with implicitly associated labels, ensure that the label is properly positioned.
The following checkbox has an implicit label that is positioned incorrectly.
Use W3C technologies when they are available and appropriate for a task and use the latest versions when supported.
This test is covered by the test to check for markup for checkpoint 3.1.
Avoid deprecated features of W3C technologies.
This test is covered by the test for popup windows that inserts the deprecated target attribute.
Divide large blocks of information into more manageable groups where natural and appropriate.
The following has two select elements; one provides appropriate grouping, the other doesn't.
Provide metadata to add semantic information to pages and sites.
No metadata has been specified on this page.
Provide information about the general layout of a site (e.g., a site map or table of contents)
No sitemap or table of contents for the site has been provided on this page.
No test cases have been provided for the following priority 2 checkpoints:
[Back to Priority 2 Checkpoints | Back to the top of the page]